About Cloudentity IDP
Cloudentity IDP (CIP) is natively supported by Cloudentity as an Identity Provider, which means that it has a dedicated connection template in Cloudentity for your convenience. Since this IDP is provided by Cloudentity, the integration is simple and seamless.
The authorization flow with Cloudentity connected to CIP looks as follows:
-
Client app tries to log in to Cloudentity.
-
Cloudentity redirects the user to CIP.
-
CIP authenticates the user and asks for consent to share data with Cloudentity.
-
CIP calls Cloudentity’s
/login/acceptendpoint after successful authentication. -
Cloudentity asks for user consent to share data with the client app, unless the client app is marked as trusted or the requested scopes were already granted for this app.
-
Cloudentity issues the tokens to the client app. Cloudentity tokens are minted based on the incoming CIP tokens with claims mapped to Cloudentity’s authentication context.
The following steps in the flow are optional:
- Cloudentity only asks for consent if the client application is not marked as trusted and requests scopes which were not granted previously (or scopes for which the user’s consent has been withdrawn).
Prerequisites
- CIP must be configured to use Cloudentity as described in Integrating Cloudentity with Identity.
Connect Cloudentity IDP in Cloudentity
Basic Configuration
-
In your workspace, go to Identity Providers > Create Connection.
-
Select the Cloudentity IDP template and click Next.
-
In the Cloudentity IDP form, enter the Name and Login URL.
Parameter Description Name Name for your Cloudentity’s Cloudentity IDP connection. This name allows users to identify the IDP they need to authenticate with. Login URL URL pointing to the address of the CIP instance you’re integrating with. Use the base URL only, as in https://example.com. -
Save your changes. Client ID, Client Secret, and Issuer URL are generated. Use them to complete the integration on the CIP side.
-
Optionally, enable Authentication context caching.
Tip
You can enable the authentication context caching if you wish to store the user’s authentication context locally. If you do, specify the cache Time To Live as well. Learn more by reading Stateful authorization with Cloudentity.
-
Select Save.
Result
Your new IDP connection is created. Users can now authenticate via the OIDC-compliant IDP.
Configure Advanced Settings
-
From the Identity Providers > YOUR_IDENTITY_PROVIDER > Configuration page, select Advanced settings at the bottom.
-
In the Authentication Method Reference, you can select an authentication method to be written into the
amrobject returned by the IDP. Theamrobject is created if it doesn’t exist. If it exists, its values are replaced with the selected item. -
Select Save.
Add Custom OIDC IDP Attributes
If your Cloudentity IDP returns custom claims outside of the default scope, make sure to add them to the IDP connector so that they can be recognized and mapped to the authentication context.
-
Go to Identities and select an IDP from the list.
-
Open the Attributes page. A standard list of OIDC attributes returned by this IDP appears.
-
Select Add attribute.
-
Fill in the form.
Option Description Attribute name Name of your custom attribute matching the incoming IDP claim Display name User-friendly name for the custom attribute Data type Data type matching that of the incoming IDP claim Claim names with a . character
If the incoming attribute has a
.character in the name, the dot must be explicitly escaped using\.when defining the IDP attribute. For example, claim namehttps://example.com/groupsmust be entered ashttps://example\.com/groups. -
Save your changes and proceed to mapping the attributes to the authentication context.
Map IDP Attributes to Authentication Context
If you’ve added custom attributes for an IDP, you need to make sure they are mapped to the {{< product-name acp >}} authentication context. You can do it either from the IDP configuration page (as explained here) or use Data Lineage instead.
Default OIDC/SAML attributes are mapped out of the box.
-
Go to Identity Providers and select an IDP from the list.
-
Open the Mappings page. A standard attribute mapping for this IDP appears.
-
Select Add mapping and map any custom IDP attributes to an existing authentication context attribute.
Note
If you need to create new authentication context attributes, read the Managing Authentication Context.
-
Optionally, you can enrich authentication context before issuing the token to the client. Attributes returned by the script do not need to be separately mapped to the authentication context.
-
Save your changes. Your mapped custom attributes should now be shared in the ID token issued to your client application, given that the target application requests them (you can check this in Data Lineage).
Connect Extensions to your IDP
-
Go to Identity Providers > YOUR_IDP > Extensions.
-
Assign a Post Authentication script to the IDP. This script will be executed upon user authentication via this IDP.
-
Connect your application to the IDP in the Post Authentication application field. Users will be redirected to this application upon authentication via this IDP.
Feature flag
Post Authentication applications must be explicitly enabled in your tenant using the
custom_appsfeature flag.
Test Cloud Identity Plane
Prerequisite
Your provider is configured as a user-authentication method by your administrator. Demo workspace is available.
Test
-
Open the user portal.
-
Select LOGIN TO DEMO APP.
-
Select your configured IDP and, next, authenticate in IDP.
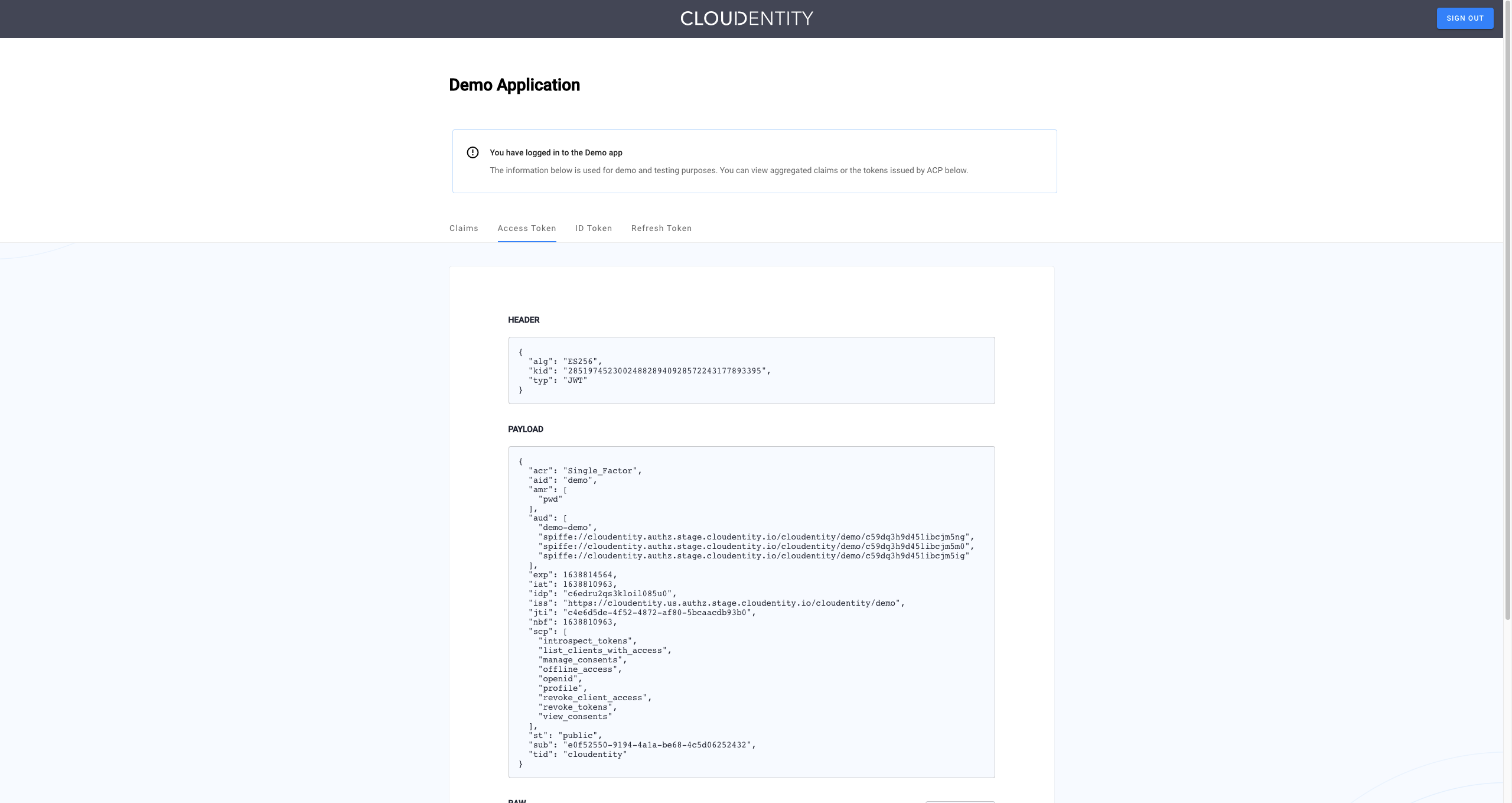
Result
Cloudentity displays the consent page that lists data scopes to be shared with the application. When you proceed to the application (ALLOW ACCESS), the PII data coming from IDP is delivered through the access token and the ID token generated by Cloudentity.
Read More
For information on granting and managing Cloudentity consents, see Cloudentity OAuth consents.