Cloudentity Integration with Kusk API Gateway
The latest release of the Kusk API Gateway features integration with Cloudentity authorization platform. This allows developers to easily leverage their OpenAPI (Swagger) specifications, to implement policy-based access control for their Kubernetes services.
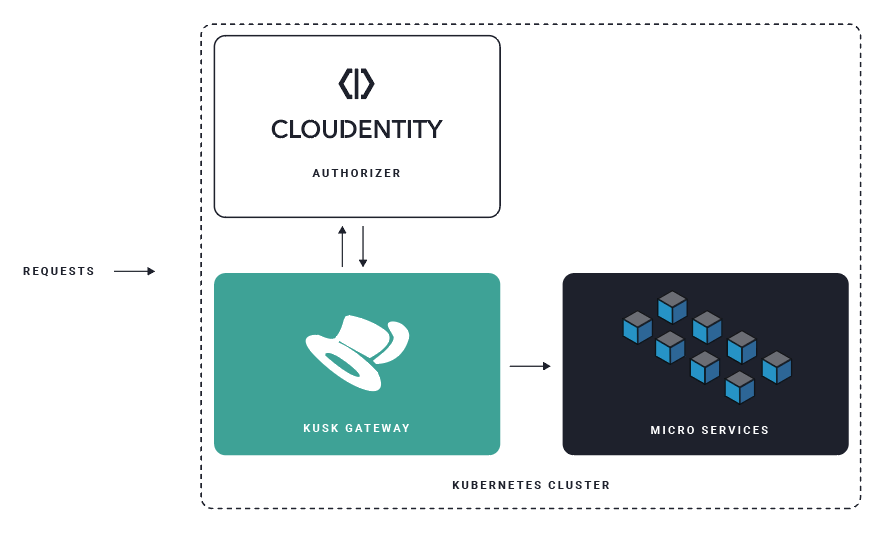
Kusk API Gateway in a Nutshell
The Kusk API Gateway is a Kubernetes-native API gateway based on the Envoy proxy. Kusk is OpenAPI-driven, making it possible to easily validate, deploy and monitor REST APIs in a Kubernetes cluster.
The Kusk Gateway uses the ubiquitous OpenAPI specification file as a single source of truth for making an API available to consumers, which includes routing configuration, request validation, timeouts, etc. Thanks to Kusk Gateway and the industry-standard OpenAPI (Swagger) specification, you can quickly publish your APIs deployed in Kubernetes without having to add any additional configuration resources, which plays nicely with both manual and automated/GitOps-based development workflows.
Kusk Gateway enables you to design and deploy your APIs from a single OpenAPI definition, allowing you to:
- Rapidly prototype your REST APIs by mocking your API responses, allowing your teams to instantly start building on top of your APIs without your services being implemented
- Enable automation of the entire deployment process of your API without requiring manual DevOps intervention
- Protect your endpoints with automatic request and response validations
- Delegate API access-control to the Cloudentity authorization platform
External Authorization Benefits
As applications become API-centric, it becomes essential to focus on the data that is exposed in the contract via the APIs, along with the governance, authorization and visibility into data access by numerous consuming applications. Authorization should be externalized, centrally managed, and flexible enough at runtime to be moved away from the core business logic itself. Owners of the data that is being shared via APIs should be able to monitor all data requests and apply sufficient authorization controls over requested data in a flexible manner, especially in this era of very fast evolving data sharing specifications across various jurisdictions.
The Cloudentity authorization platform provides a centralized, externalized and flexible way to provide authorization capability for business applications with all the required governance and real time visibility for data access protection for the GraphQL ecosystem.
The Cloudentity authorization platform enables application developers to:
- Eliminate the need to embed data-authorization policies into REST services
- Decouple hard-to-audit local enforcement rules and move them to a centralized location
- Manage, govern, and enforce the externalized authorization rules independently of the application development
It enables applications to:
- Transitively support advanced data authorization requirements, including role based access control (RBAC) and attribute based access control (ABAC) style models, without any modification to application code
- Readily comply with data sharing and privacy controls in emerging OpenData standards such as Open Banking, Open Energy, Open Insurance, and more.
- Define and maintain all the authorization rules to be enforced as policies that allow policy approval, review, and other governance process.
- Utilize “Authorization as a service” offering either from Cloud or in a hybrid or on-prem model
Finally, the Cloudentity authorization platform enables:
- Application security engineers to have more visibility to platforms that are requesting data and enforce conditional policies to restrict based on various conditions.
- Application authorization policies to be defined in a declarative format, which can be propagated across environments using modern CI/CD and DevOps pipelines.
Kusk with Cloudentity - a Simple Demo
The integration of the Kusk API Gateway with Cloudentity authorization platform makes it easy to delegate policy-decisioning from the Kusk API Gateway to the Cloudentity authorization platform. This demo shows just how easy it is.
Prerequisites
You will need:
- Kubernetes version 1.19 or subsequent
- A running Kubernetes cluster
- Helm version 3.0 or subsequent
- Kusk CLI version 1.2.0 or subsequent
- Cloudentity tenant
For detailed instructions on setting up the prerequisites, you can refer to Protecting APIs on Kusk Gateway.
Install the Kusk API Gateway in Kubernetes
This first step is to install the Kusk API Gateway in your Kubernetes cluster. Kusk is a Kubernetes-native application, making this an easy task to accomplish:
kusk cluster install --no-dashboard --no-api
✔ Looking for Helm...
✔ Adding Kubeshop repository...
✔ Fetching the latest charts...
✔ Installing Kusk Gateway
✔ Installing Envoy Fleet...
• --no-api set - skipping api installation
Install the Cloudentity Authorizer
Next, follow the instructions in Protecting APIs on Kusk Gateway to create the API Authorizer. The QuickStart page will show a Helm invocation to install the authorizer in your Kubernetes cluster, with the client credentials properly set up for your authorizer:
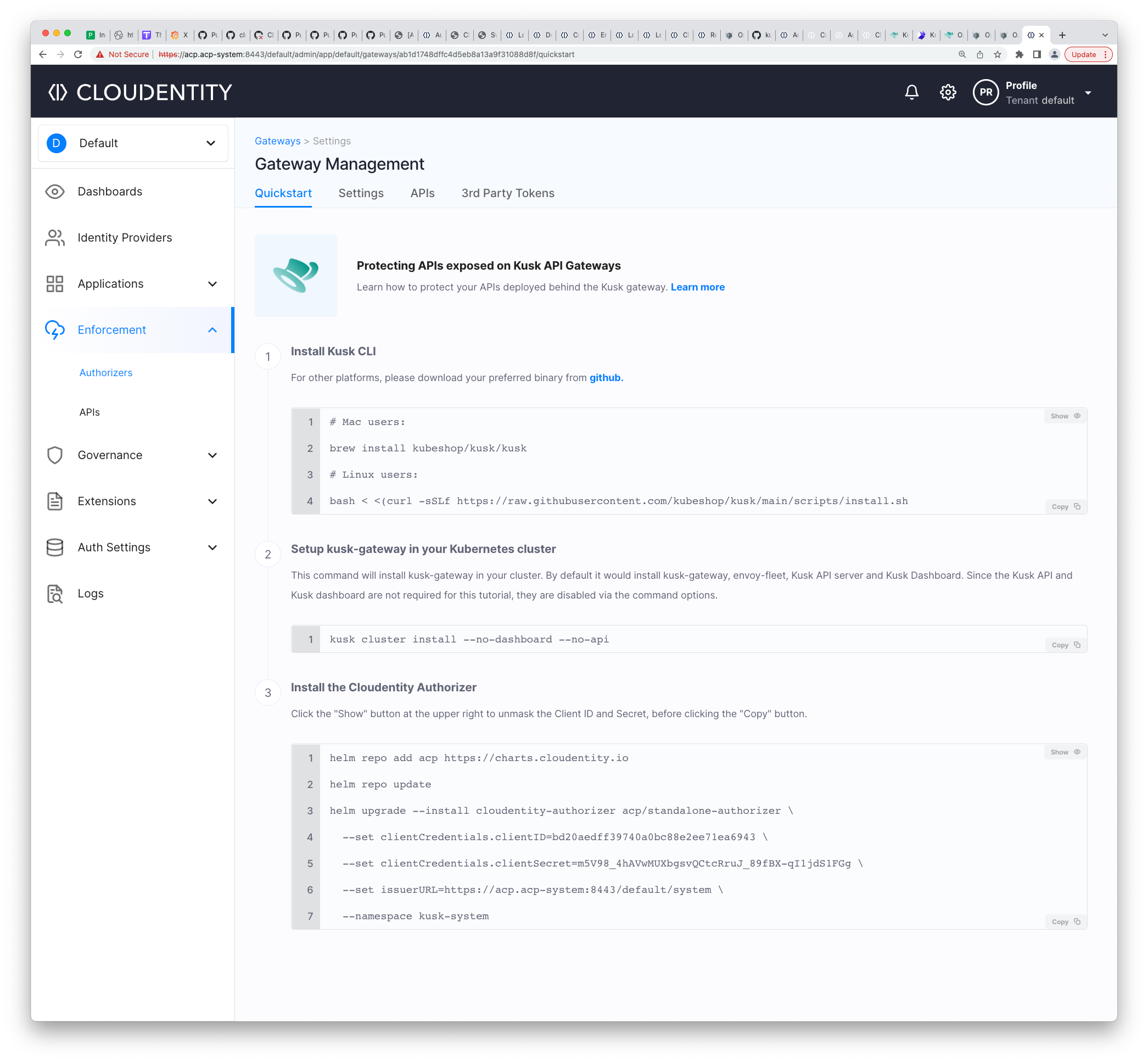
You can install the Authorizer using the following command:
-
{client-id}and{client-secret}are the credentials of your authorizer created in Cloudentity -
{tid}and{aid}are tenant and workspace IDs, respectively -
The parameters are visible in the command displayed in your Cloudentity tenant’s Authorizers menu
helm repo add acp https://charts.cloudentity.io
helm repo update
helm upgrade --install cloudentity-authorizer acp/standalone-authorizer \
--set clientCredentials.clientID={client-id} \
--set clientCredentials.clientSecret={client-secret} \
--set issuerURL=https://{tid}.authz.cloudentity.io/{tid}/{aid} \
--namespace kusk-system
Release "cloudentity-authorizer" does not exist. Installing it now.
NAME: cloudentity-authorizer
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Sep 23 12:33:54 2022
NAMESPACE: kusk-system
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
Install a sample REST Service
For the purpose of this demonstration, we are going to install the popular httpbin service. You can find this manifest in the acp-on-k8s repository:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cloudentity/acp-on-k8s/master/examples/httpbin/deployment.yaml
serviceaccount/httpbin created
service/httpbin created
deployment.apps/httpbin created
Deploy the sample API to the Kusk Gateway
Kusk is OpenAPI-driven, so to deploy our httpbin service, we only need to provide an OpenAPI
specification, with suitable extensions.
-
For the purpose of this demo, we use a spec that only exposes the
GET /anythingendpoint. Save it underapi-httpbin.yaml.openapi: 3.0.0 info: title: httpbin-api description: HTTPbin api version: '0.1.0' x-kusk: upstream: service: name: httpbin namespace: default port: 80 mocking: enabled: true auth: cloudentity: host: hostname: cloudentity-authorizer-standalone-authorizer.kusk-system # default authorizer service, change in case your authorizer is installed differently port: 9004 paths: /anything: get: produces: - application/json responses: "200": description: Anything passed in request summary: Returns anything passed in request data. tags: - AnythingNote that the
x-kuskelement contains anupstreamobject that points to ourhttpbinservice, and anauthobject, which delegates API authorization to the Cloudentity authorizer. Kusk standards can change, though - if you face issues related to this specification, please consult Kusk documentation. -
To deploy this Service to the Kusk gateway, we simply invoke the extended specification above:
kusk api generate -i api-httpbin.yaml | kubectl apply -f -api.gateway.kusk.io/httpbin-api createdThe API defined by this OpenAPI specification will have been synced to Cloudentity, via the Kusk-Cloudentity integration:

-
To exercise our newly-deployed API, we will create a local port-forward to the Kusk Gateway:
kubectl -n kusk-system port-forward service/kusk-gateway-envoy-fleet 7080:80And then curl the local port:
curl -D - -X GET http://localhost:7080/anythingHTTP/1.1 200 OK x-kusk-mocked: true content-type: application/json content-length: 30 date: Fri, 28 Oct 2022 10:54:45 GMT server: envoy {"message":"Mocked Response!"}% -
Next, lets define a policy of the API Request type using REGO. Use the Cloudentity’s REGO Policy Editor, with the following definition, which requires the request to have a custom header
REGULAR_USER:package acp.authz default allow = false allow { input.request.method == "GET" input.request.headers["X-Custom-Header"][_] == "REGULAR_USER" } -
Now, we can attach this policy to the
GET /anythingendpoint under Enforcement > APIs > Policy assigned: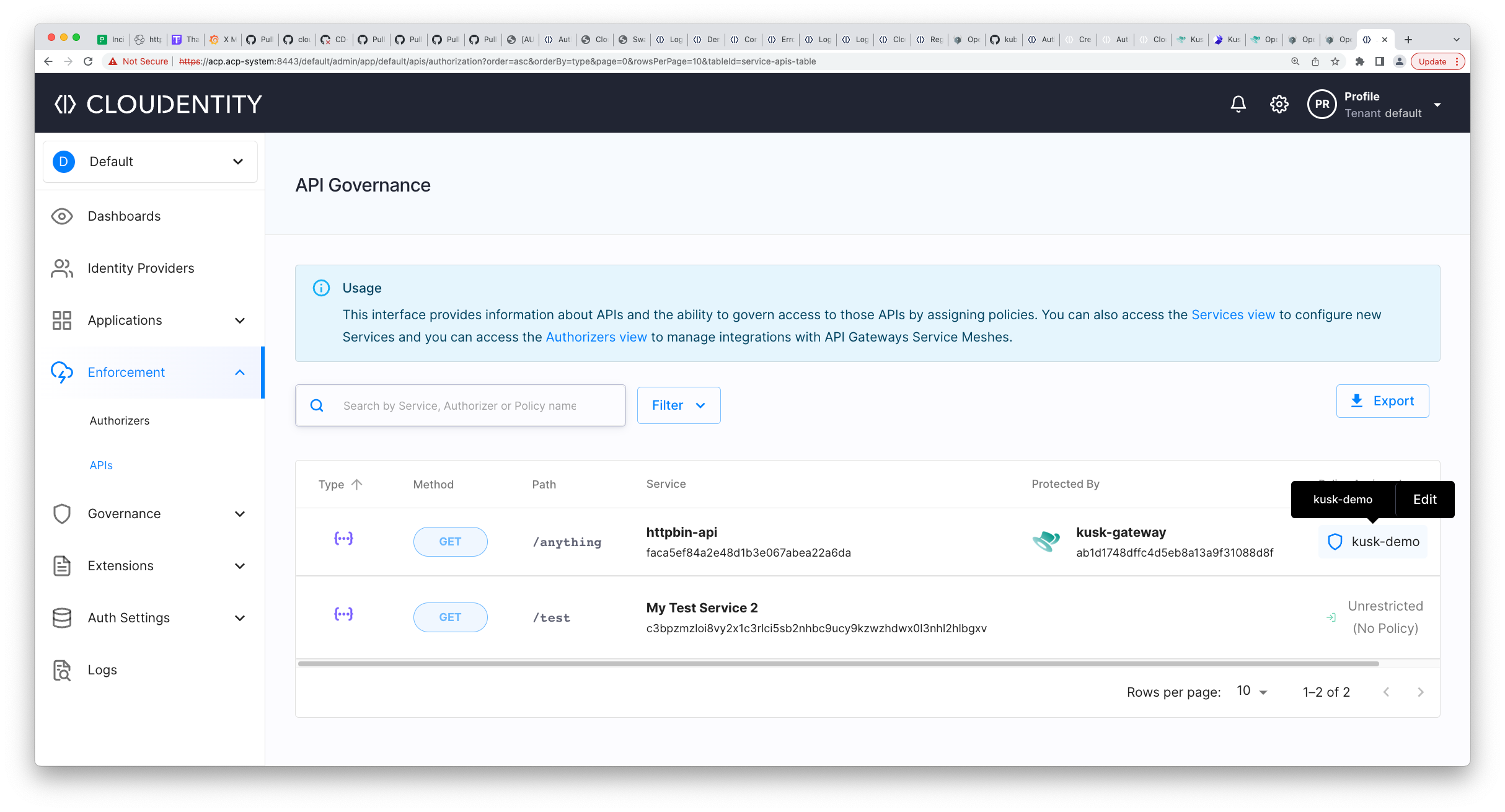
After attaching the policy, access is now rejected:
curl -D - -X GET http://localhost:7080/anythingHTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden date: Fri, 23 Sep 2022 23:14:17 GMT x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 5 server: envoy content-length: 0But, if we add the custom header that the REGO policy requires, the request is authorized again:
curl -D - -X GET http://localhost:7080/anything -H "X-Custom-Header: REGULAR_USER"HTTP/1.1 200 OK x-kusk-mocked: true content-type: application/json content-length: 30 date: Fri, 28 Oct 2022 11:22:26 GMT server: envoy
Conclusion
We have seen how the Kusk API Gateway leverages the OpenAPI specification, to make it easy to deploy and protect that REST APIs of your Kubernetes services. Kusk integration with Cloudentity makes it especially easy to delegate API-authorization to the Cloudentity authorization platform, which brings the key benefits that:
- API Authorization policy need not be implemented in the REST services themselves.
- Authorization policies are centrally administered, with benefits to auditability and ease of management.
- Cloudentity’s authorization platform provides convenience and flexibility in defining policies.
Like what you see? Register for free to get access to a Cloudentity tenant and start exploring our platform!

