Client Secrets Overview
Client secrets are a crucial part of the client application credentials. It is a secret known only to Cloudentity and the client application. They are used, for example, along with the client identifier, to provide client credentials to authenticate the application to Cloudentity in order to get an access token.
To illustrate what client secrets are and why they are used, lets look at the following example. A client application is registered in Cloudentity. It has its credentials defined. The application wants to access the APIs of another web application in a machine-to-machine environment. The application is configured to use the client credentials OAuth grant flow. To get a token, the client application presents its credentials - a client identifier and a client secret. Cloudentity verifies if the credentials from the request match the credentials of the registered client application to prevent the situation that an unauthorized malicious application would get an access token by, for example, impersonating other client application.
Security Considerations
It is crucial for client secrets to store and manage them secure enough to prevent unauthorized access to APIs, because they are used to get access tokens that allow applications to access APIs. Client secrets must be sufficiently random so they cannot be guessed. They should not be stored in distributed native applications and single-page JavaScript applications (as they can be decompiled and the client secret may become exposed).
As client secrets may become exposed, it is a good practice to keep them short-lived. Cloudentity makes it possible to rotate client secrets.
To store secrets in a safer manner, Cloudentity gives you a possibility to store client secrets as a one way hash.
Client Secret Rotation
When you rotate a secret, a new secret is created for your application and the previous one is added to the list of rotated client secrets. Such a list can store only one rotated client secret (by default). If the list already contains a client secret when you rotate secrets, the previous rotated client secret is revoked and the new rotated client secret is added.
Note
For on-premise deployments, it is possible to configure how many rotated client secrets are stored. To change it, provide the number of your choice as the value for the
max_number_of_client_rotated_secretslimit in your Cloudentity configuration file (config/config.yaml).
Rotated client secrets are still active and valid. If you wish, you can revoke them. Revoking a secret means that it is not possible to use them anymore. The developer must update the client secret in the application before the application can access the APIs. You can revoke all rotated secrets either in the Viev previously used secrets modal in your application settings or by using the Cloudentity revoke client secrets Admin API.
One-way Hash Secrets
One-way hashing of client secrets provides additional security when it comes to storage of the secrets. Hashing a secret hides the plaintext OAuth credential value and makes it impossible to be read both in the interface and the database.
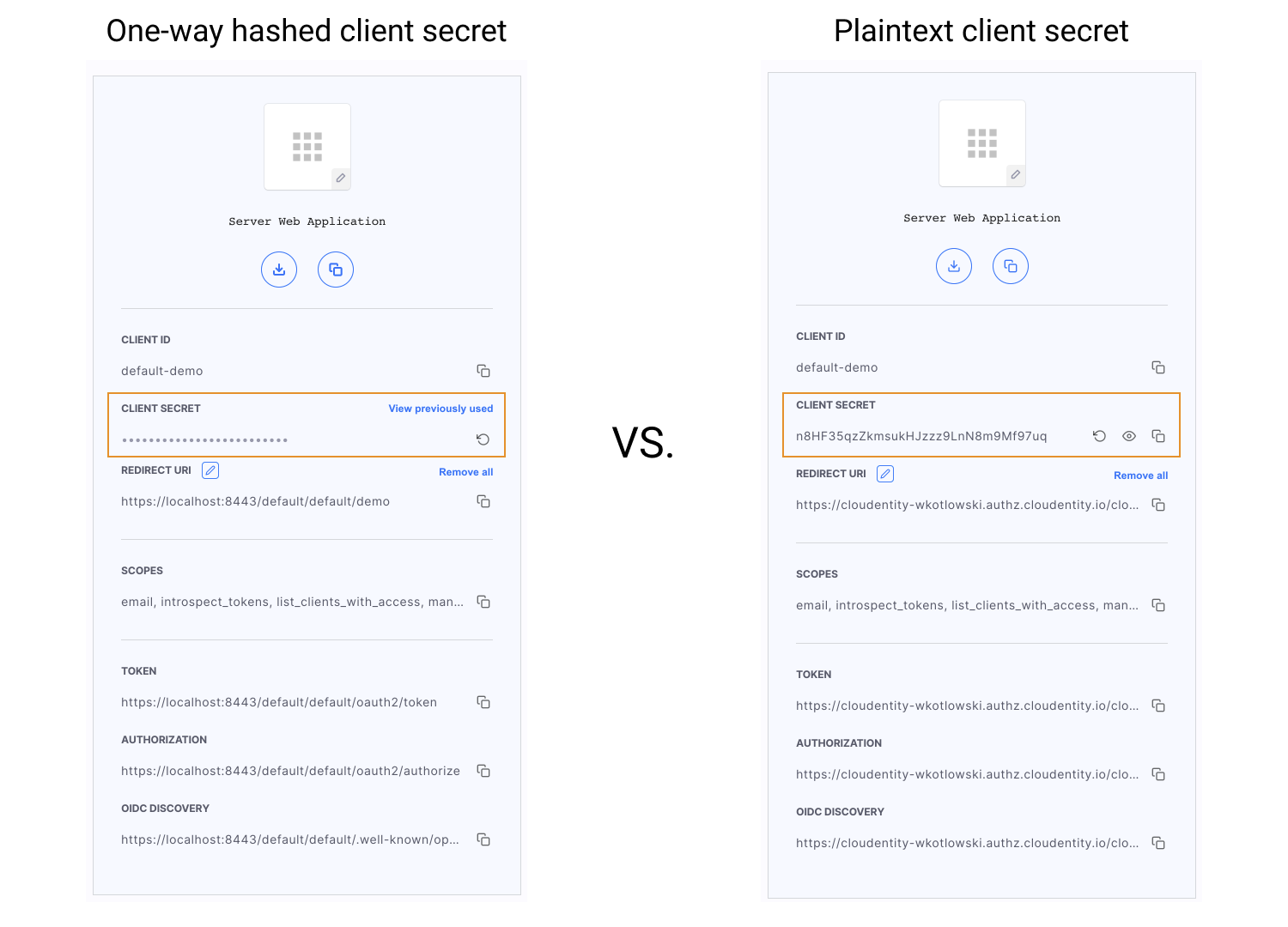
In Cloudentity, client secrets are hashed using the SHA256 algorithm. There are only two situations when the client secret can be read:
-
During the creation of a client (either in the UI or in the request response if using API)
-
When you rotate a secret (either in the UI or in the request response if using API)
Tip
If you are using UI, for both cases you are reminded to either copy or download your client secret, as you won’t be able to view it again.
One-way hashing is currently available only for the customers who deploy their
Cloudentity on premise.
To enable one-way hashing of client secrets, you need to set the
client_secrets_stored_as_one_way_hash feature flag to true in your Cloudentity
configuration settings.
On-way Hashing Impact on Cloudentity Authorizers
Every time you create an authorizer, a corresponding client application is created for your authorizer in your System workspace. For multi-tenant authorizers, it is created within the system tenant’s System workspace. For single-tenant authorizers, the client is created within the system workspace for your tenant.
When you are using one-way hashing for secrets:
It is not possible to display a plaintext secret for your authorizer’s client application
The logic responsible for generating the configuration for your authorizer is not able to fetch the secret, as it is hashed. For example, if you are using Istio Authorizer, your configuration file would look like the following:
resources: - manifest.yaml secretGenerator: - name: istio-authorizer-secrets namespace: acp-system literals: - CLIENT_ID=c5fk2d1ngvl012k9noog - CLIENT_SECRET=To be able to configure your authorizers and enable them to enforce access control, you must rotate the client secret for your authorizer’s client application. Then, copy/download the secret and use it in your authorizer’s configuration.