About Configuring Cloudentity Platform
Configuration Reference
To learn about every available setting, see Cloudentity Configuration Reference.
Any of the reference options can be used in Helm Charts. Cloudentity provides an easy way to provide required parameters via dedicated keys as well as optional ones via the custom config. For secrets, there is a special secret config which could be used to store passwords.
Required parameters
Those parameters are required for Cloudentity to start succesfully. For datastores, any key from the reference configuration can be provided.
-
Server URL is a public address on which Cloudentity listens for incoming requests
serverURL: "https://acp.example.com:8443" -
SQL database
sql: type: "postgresql" url: "postgres://root@cockroachdb-public.cockroachdb:26257/acp?sslcert=%2Ftls%2Ftls.crt&sslkey=%2Ftls%2Ftls.key&sslmode=verify-full&sslrootcert=%2Ftls%2Fca.crt" -
Redis database
redis: addrs: - "redis-master.redis:6379" redis_search: true tls: enabled: true ca: "/tls/ca.crt" key: "/tls/tls.key" cert: "/tls/tls.crt"
Optional parameters
Any configuration option from the configuration reference can be provided in this config. It can be merged with default values and the ones provided in other configuration blocks defined here.
config:
create: true
name: acp-data
data:
logging:
level: debug
Secrets
It is the same as optional parameters section, but paremeters are saved to K8s Secret instead of
the ConfigMap.
secretConfig:
create: true
name: secret
data:
system:
secret: mysecret
Features
For convenience, Cloudentity feature flags are defined under seperate key. You can specify here any of the features from reference config.
features:
dev_mode: true
demo_app: true
You can enable/disable System Features or Tenant Features.
For all available feature flags, check the features section in the Cloudentity Platform Configuration Reference.
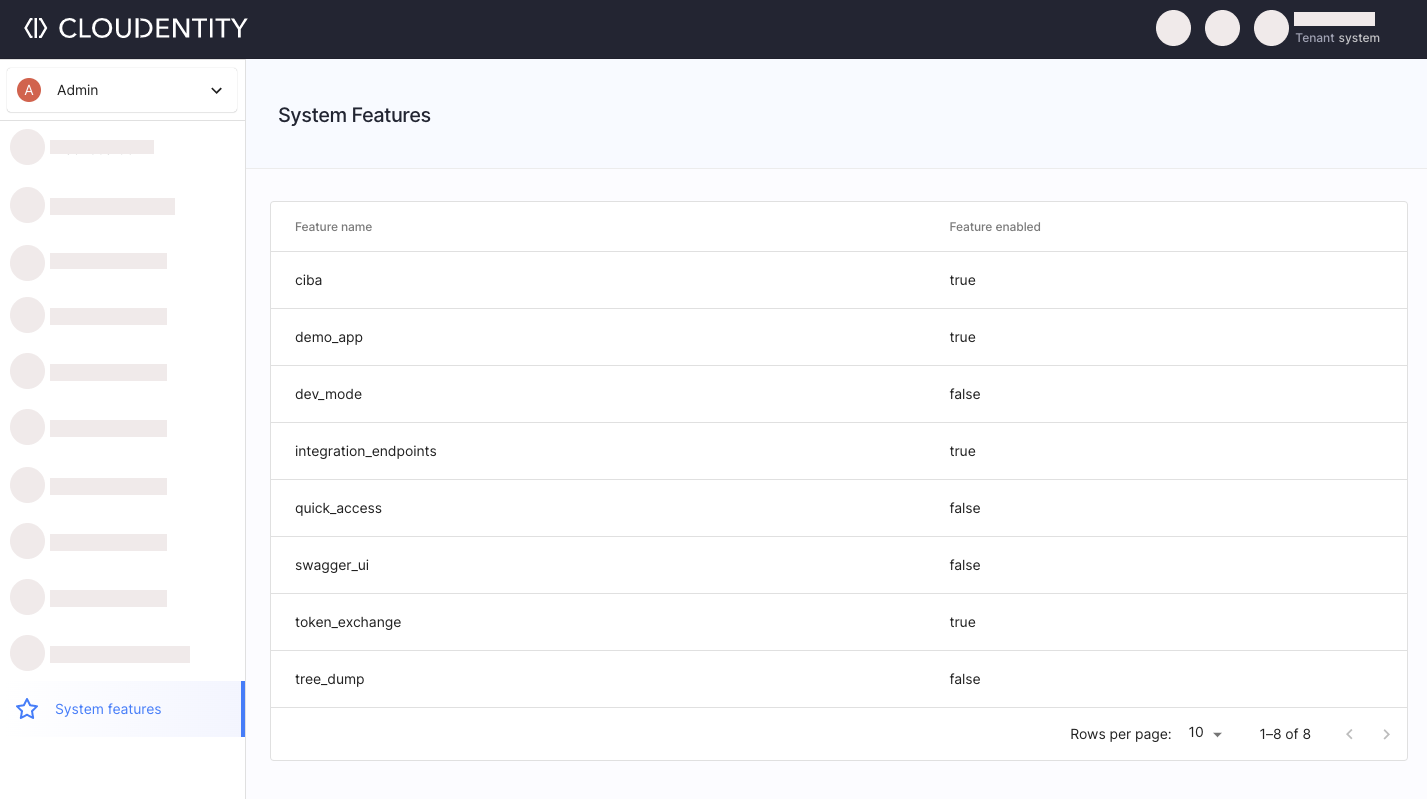
System Features
You can enable System feature flags globally for all tenants within the deployment by
configuring them in the features section of the Helm Chart.
You can distinguish system feature flags by looking at the comments next to the feature flag
looking for (system).
Example:
[...]
features:
integration_endpoints: true
login_with_select_account: false
script_transformer: true
admin_workspace_access: false
system_workspace_access: false
ciba: true
token_exchange: true
webauthn: true
user_self_registration_improved: true
[...]
Enabling a system feature flag means that the feature is enabled for all tenants within the
deployment. For example, if ciba is set to true all tenants can use the Client-Initiated Backchannel Authentication Flow (CIBA).
You can view enabled system features in the Admin Workspace of the System Tenant.
System Tenant Access
For default Cloudentity on Kubernetes deployments, you can find the System Tenant under the
https://acp.acp-system:8443/system/admin/app/URL and login using admin as a username and system tenant secret as the password (found in configuration file undersystem.secret,n8HF35qzZkmsukHJzzz9LnN8m9Mf97uqby default).
Tenant Features
Tenant feature flags can be turned on either in the features section of the Helm Chart, or in the
Tenant Management view in the Admin Workspace in the System Tenant.
System Tenant Access
For default Cloudentity on Kubernetes deployments, you can find the System Tenant under the
https://acp.acp-system:8443/system/admin/app/URL and login using admin as a username and system tenant secret as the password (found in configuration file undersystem.secret,n8HF35qzZkmsukHJzzz9LnN8m9Mf97uqby default).
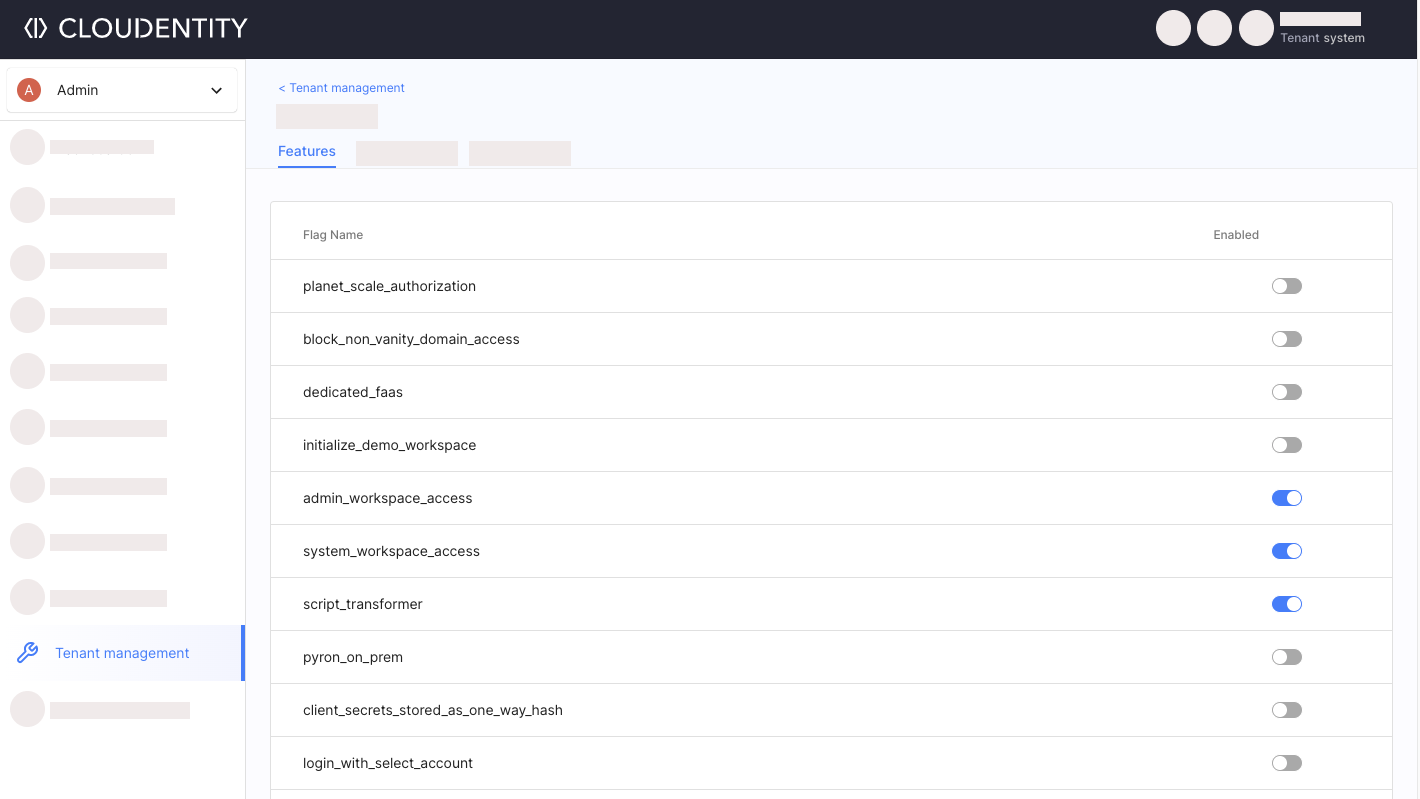
Enabling a tenant feature flag means only this particular tenant can use the enabled feature.
Advanced parameters
Those paremeters are considered for advanced use case or developer mode.
-
Disable TLS in every Cloudentity component. This could be usefull in istio integration where TLS is already provided by envoy.
tlsDisabled: true -
If you are using dedicated mTLS ingress, additional listen address must be provided.
serverURLMtls: "https://mtls.acp.example.com:8443" -
Cloudentity startup command can be configured, full list of parameters is available here.
args: - server - start - --metrics
Paremeters Merge Order
Parameters are merged from each configuration file including reference config. The order of merge is as following with bottom one taking priority in case of conflict.
- reference config (part of Cloudentity docker)
- standalone parameters like redis, sql, features, and more (
/data/config.yaml) - optional parameters config (
/data/extraconfig.yaml) - secret config (
/secret/config.yaml) - environment variables
This is controlled by the configPath parameter with default value of /data/config.yaml,/data/extraconfig.yaml,/secret/config.yaml
Using External Config
In case where you would want to manage secrets on your own, you could do that by disabling secret
creation and providing secret name with key config.yaml.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
type: Opaque
metadata:
name: secret
stringData:
config.yaml: |
system:
secret: mysecret
secretConfig:
create: false
name: secret
You can customize secret keys or provide multiple keys, it will requires update of configPath.
In this example system.yaml secret will be used as Cloudentity config while
cert.key will be mounted under /secret/cert.key for further use.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
type: Opaque
metadata:
name: secret
stringData:
system.yaml: |
system:
secret: mysecret
cert.key: <data>
secretConfig:
create: false
name: secret
configPath: /data/config.yaml,/data/extraconfig.yaml,/secret/system.yaml